Wind Turbine Design
Wind turbines are one of the many renewable energy sources that have been developed in recent decades. These massive structures that dominate the landscape have become increasingly common in many regions of the world. But whether it is a wind turbine kit for the roof of your home or an off-shore generator, wind turbine design is not something simple! Each design requires a great deal of experience and expertise. We have created this post on the subject of wind turbine design to explain everything you need to know about this topic.
Wind Kinetic Energy
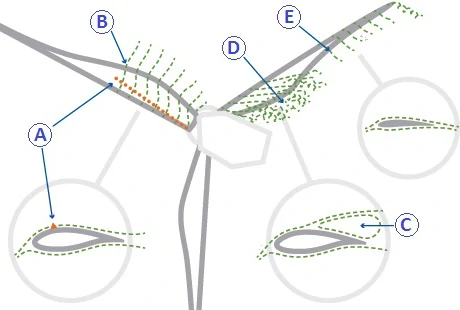
Wind turbines operate by converting wind kinetic energy into electrical energy. They consist of three main parts: the nacelle that contains the electrical system and transmission, the hub in which the rotor is located, and the blades that rotate together with the rotor. Wind turbine design is complex and requires several technical skills. The first crucial step is to choose the location of the site where the turbine will be installed. The key factor to consider when choosing the site is wind speed. In general, sites with average wind speed should be chosen since wind turbines will exert their best efficiency there.
What are usually the Sites chosen to build Wind Turbines?
Ideal sites for wind turbine construction are usually those exposed to constant and strong winds. These include coastal areas, hilltops, and vast, open flat areas. Coastal areas are particularly advantageous because of the presence of constant marine winds. Hilltops, on the other hand, are often chosen because the wind accelerates as it rises up a hillside (Venturi effect). Large flat areas allow the wind to move freely without obstruction, making them ideal for wind turbine construction.
Design of the Rotor and Blades of Wind Turbines
The rotor design of wind turbines is done to maximize their energy efficiency. In fact, the blades of wind turbines are made of materials such as carbon or glass-resin because they allow for the construction of blades that are large and light at the same time. Each blade must be perfectly balanced to ensure smooth rotation of the turbine. Any imbalance would in fact cause increased vibration and reduce the efficiency of the turbine. In addition, the shape of the blades is carefully designed to ensure controlled airflow through them.
Transmission in Wind Turbine Design
Transmission allows the turbine to convert the wind’s kinetic energy into electrical energy. This is because the transmission system inside the turbines transmits the rotary motion of the blades to the power generator. The transmission of the wind turbine must be designed to provide a very efficient transmission. Precisely for this reason a series of gears, more or less similar to those of a car’s transmission, ensure a proper ratio.
The Electric Generator
The generator of a wind turbine is what converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The performance of a wind generator depends on multiple factors, including wind speed, the efficiency of the turbine design, and the leaping area of the blades. In terms of power output, a wind generator can range from a scale of a few kilowatts (KW) if we are talking about home kits, up to several tens of megawatts (MW) for large wind farms. Average performance is around 30-45% of maximum output, due to natural fluctuations in wind speed.
Control Technology
The control of the wind turbine is essential during its design. Variation in wind speed has a significant impact on the efficiency of the turbine. Blade angle control technology, which can be adjusted manually or automatically, ensures maximum turbine efficiency at any wind speed and limits the effects of wind gusts. And you have certainly noticed that in high winds the turbines are stationary. Another crucial aspect of wind turbine control is efficiency and calibration monitoring. This allows the performance of the turbine and its tuning to be updated.

3 thoughts on “Wind Turbine Design”
Comments are closed.